What is Blood Pressure
When your heart beats, internally it is pumping blood to your body tissues and cells. This is the heart’s way to supply oxygen and energy to body cells through blood. Therefore as the blood moves into arteries, the blood pushes against the wall of blood vessels. And the strength of this pressure of blood stream towards wall of your artery blood vessels is called blood pressure (BP).
The heart is the strongest muscle in our body which pumps blood around the body constantly during every second of your lives. Heart pumps the Blood with low oxygen level towards lungs so that the lungs replenish oxygen supplies in it. Then the Heart pumps this blood rich with oxygen throughout the body muscles and cells.
In this article, I will explain what is blood pressure, causes of high BP (HBP), symptoms, risks, diagnosis and measurement of HBP, what blood pressure number reading means and how to prevent high BP. A raised BP means extra strain on your arteries and your heart and this may lead to serious health complications including heart attacks and strokes.
What do the BP Numbers Mean?
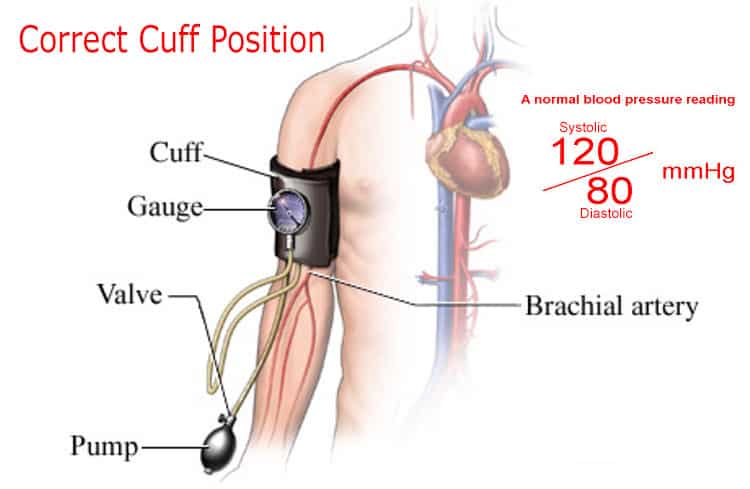
We record blood pressure with two numbers i.e. the Systolic Pressure (Higher Number) and the Diastolic Pressure (Lower Number). And the unit to measure BP is millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Systolic Blood Pressure (Higher Number in Reading)
A systolic pressure is the pressure of blood stream on wall of blood vessels when your heart beats and pumps oxygenated blood towards your body cells. (when the heart muscle contracts). This is the higher number and written first in your BP measurements.
Diastolic Blood Pressure (Lower Number in Reading)
A diastolic pressure is the pressure of blood stream on wall of blood vessels when blood from your body cells goes back to heart (when the heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood). This is the lower number and written second in your BP measurements reading.
So if your BP is 120/80, here 120 mmHg is the Systolic Pressure and 80 mmHg is your Diastolic Pressure.
How Can You Tell if You Have High BP (Hypertension)
More than one in four of adults in the United Kingdom have high BP, although many of them won’t realize it. High BP (hypertension or HBP) usually does not have any specific symptoms or something that you feel or notice. It does not tend to produce obvious signs or symptoms you can feel easily. You can only know if you have increased BP (hypertension) by getting your BP measured.
As per the American Heart Association, we should consider a BP normal if it is less than 120/80. Below is a general range definition of BP and associated conditions according to American Heart Association:
Low Blood Pressure (Hypo-tension)
Lower than 90/60 mmHg – If your BP is less than 90/60mmHg we should consider it as low BP.
Normal Blood Pressure
90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg – If your BP ranges between 90/60mmHg and 120/80mmHg, we will consider it as normal BP.
Pre High BP (Pre-Hypertension)
120/80 mmHg to 139/89 mmHg – If your BP ranges between 120/80 mmHg and 139/89 mmHg, we will consider it as pre-hypertension or pre-high BP. A pre-hypertension could mean that you’re at risk of developing HBP unless you take immediate steps to keep it under control.
Stage 1 High BP (Stage 1 Hypertension)
140/90 mmHg to 159/99 mmHg – If your BP ranges between 140/90mmHg and 159/99 mmHg, we will consider it as stage 1 high blood pressure. This is an alarming situation and need an immediate medicinal treatment and life style changes.
Stage 2 High BP (Stage 2 Hypertension)
Over 160/100 mmHg – If your BP is higher than 160/100 mmHg, we consider it as stage 2 HBP. That is to say this is a serious health condition which require an immediate medicinal treatment and life style changes.
Hypertension (HBP) – Risks, Side Effects and Complications
However, the BP readings can vary in a single person throughout the day based on some certain situations and factors such as foods eaten (e.g. caffeine and salt give a raise in BP), stress, anxiety and smoking etc.
Keep Your BP at Lower Side
More of the health risks associated with abnormal BP are caused by HBP than by the low BP. That is to say that higher your BP is, higher the risk of heart and other problems would be. Even if you do not have HBP developed yet, then too it is good to keep your BP as low as you can.
For example, if your BP is 135/85 mmHg, we may not consider it as HBP yet but with this reading you are twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke as with a reading of 115/75 mmHg.
There are many serious complications associated with HBP including heart disease, stroke (brain damage), kidney (renal) disease, eye damage and hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis or arteriosclerosis), if not controlled.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
Though the causes of HBP cannot be firmly classified and clear but there are some certain things which can increase your risk of high BP.
- If you are overweight
- Lack of doing enough exercise
- Having a family history of high blood pressure keeps you at risk
- People who take too much of salt are at risk of high BP.
- If you don’t eat enough fruit and vegetables
- Consuming too much of alcohol
- If you drink too much of coffee or any other caffeine-based drinks
- Smoking could raise your BP
- Not getting enough sleep or having disturbed sleep
- Being over 65 years
- If you are from African or Caribbean races
8 Side Effects and Health Risks of Caffeine (Coffee)
16 Proven Health Benefits of Coffee (Caffeine)
You can reduce chances of getting high BP by maintaining a healthy life style. A healthy life style can even lower your BP if you already have a high BP.
Risks of High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
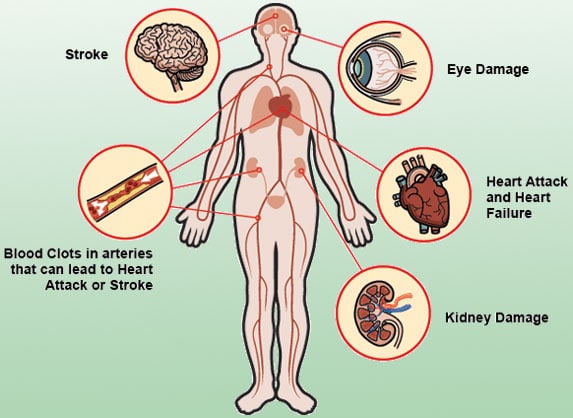
A HBP has a number of health risks associated if not taken under control. That is to say that continuous raised BP puts extra strain on heart, walls of blood vessels and other organs such as brain, eyes and kidneys.
It is very important to bring the BP under control if you have high BP. Because a persistent high BP can cause a number of serious and potentially life-threatening conditions including strokes, heart failure, heart attack, peripheral arterial disease, aortic aneurysms, kidney disease and vascular dementia
How is Blood Pressure Measured?
BP is measured with a simple medical instrument called Sphygmomanometer. Most people must have seen this device. There are two primary types of Sphygmomanometer i.e. traditional analog Sphygmomanometer and Digital Sphygmomanometer. In clinics, most doctors tend to use the traditional analog Sphygmomanometer. The digital Sphygmomanometer are mostly used by home users to keep a track record of their BP at home.
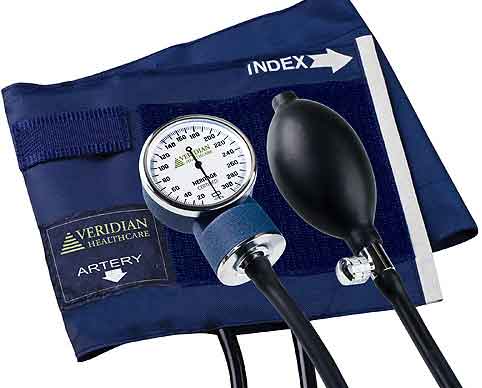
Sphygmomanometer consists of an inflatable rubber cuff that is wrapped around your upper arm during BP test. When the cuff is inflated with a pressure pump, it restricts the blood flow in your artery. Then a mercury or mechanical manometer used to measure the pressure. Sphygmomanometer instrument measures the BP in units called millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
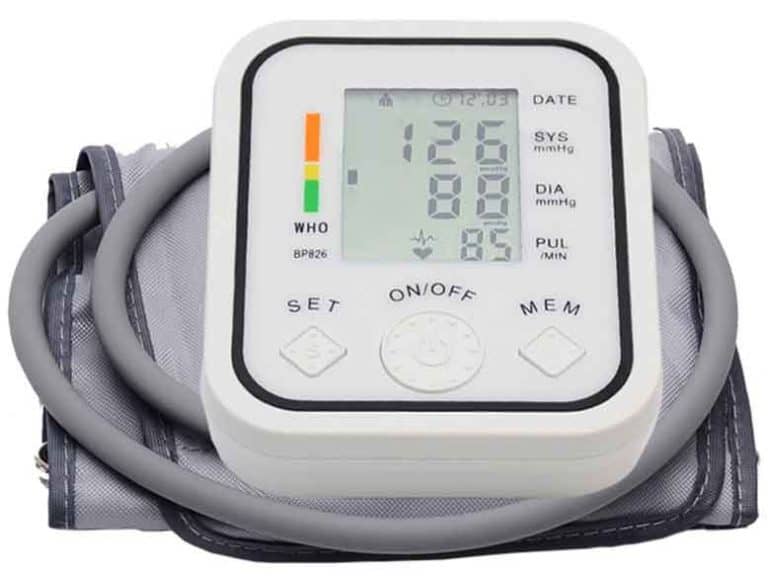
There are two types of pressures we gauge when we measure BP knows as Systolic pressure and the Diastolic pressure.
A sphygmomanometer is always used together with a means which can determine blood flow at different pressure levels. In a manual sphygmomanometer this is done by a stethoscope while in a digital sphygmomanometer some electronic sensors do the same.
Steps to Check Blood Pressure With Sphygmomanometer
Time needed: 2 minutes
Here are the steps that your doctor will do to check your blood pressure with a manual sphygmomanometer.
- The rubber cuff is placed around your upper arm.
- The arm should remain at the level of your heart at side of your body and the patient should sit up with the arm supported (resting on something).
- See the correct position of measuring blood pressure in this picture

- It is important that the size of the cuff should be appropriate. If the cuff size is too small the reading will be inaccurately high while if it is too large the reading will come too low.
- The cuff is inflated with an air pump to create a pressure in cuff. This pressure blocks the blood flow in main artery of your arm
- Once the cuff is full of pressure and blood flow in artery is stopped, the doctor starts releasing the pressure gradually.
- As the pressure decreases, the doctor will listen over the sound of artery at the front side of your elbow with a stethoscope.
- In digital sphygmomanometer an electronic machine senses the pulsation.
- The pressure at which the first pulsation from artery is heard, is your systolic pressure (the top number when writing your blood pressure).
- As the cuff pressure is decreased further, it comes to a point when the pulsation finally stops. This pressure when the pulsation is stopped is your diastolic pressure (the second and lower number when writing your BP)
- This all process is done with electrical sensors, in case of digital sphygmomanometer.
How to Prepare for Blood Pressure Test
- Do not smoke at least 30 minutes prior to the test.
- Do not drink coffee or any other caffeinated beverage for at 30 minutes prior to the test.
- Go to bathroom and urinate before the test.
- Sit and rest for 5 minutes before your BP test.
- If you are a regular BP patient and need to track your BP, don’t forget to take your log book to doctor.
How to Reduce Blood Pressure Level
This is important to decrease and keep the BP level low in your body. You can control and keep your blood pressure lower naturally with the following lifestyle changes:
- Reduce the amount of caffeinated drinks such as coffee and other energy products.
- Reduce the amount of salt in your food
- Eat healthy foods such including green leafy vegetables and fruits.

- Reduce the amount of alcohol intake.
- If you are overweight, it is important to lose weight
- Do the regular exercise
- Quit smoking
- Take proper disturbance-free sleep at night for at least 6 hours.
Weight Loss Diet – 12 Foods to Lose Weight Naturally
However, see your doctor If your BP is not controlled only with these natural therapies. Follow the medical prescriptions of your doctor properly..
Medicines for High Blood Pressure
Based on your high BP level, your doctor may recommend you taking medicine to keep your BP under control. Usually the medicine for HBP is taken once a day. For instance, the most common types of medicine to control BP may include:
- Angiotensin-2 Receptor Blockers (ARBs) – medicines such as losartan, candesartan, olmesartan, irbesartan and valsartan
- Diuretics – indapamide and bendroflumethiazide etc.
- ACE inhibitors – medicines such as enalapril, ramipril, lisinopril and perindopril
- Alpha-Blockers – for e.g. doxazosin
- Beta-Blockers – medicine such as bisoprolol and atenolol.
- Calcium Channel Blockers – These include verapamil, amlodipine, felodipine, nifedipine or diltiazem.
- Renin Inhibitors – for e.g. aliskiren
How to Prevent High Blood Pressure
You can keep your BP under control with a healthy and active life style, regular exercises, proper use of medicines if prescribed. Avoiding foods which increases the BP level such as salt, coffee (caffeinated drinks) and smoking etc. would also be recommended.
If you have already been diagnosed with HBP (Hypertension), changing only the life style may not work. And then it is important to obtain proper medical assistance. So that your doctor will prescribe you the required treatment to control your HBP.
It is really important to check your BP regularly. And if signs of high blood pressure (hypertension) are found, take steps right away to control it by changing your life style to avoid further complications.
Children should also have their BP measured starting at 3 years of age. If the signs of pre-hypertension are detected, take steps to bring it under control to avoid progressing to hypertension.
Most importantly, there are no specific symptoms of slight high blood pressure, but it starts damaging you inside even at initial stage. Hence it is very crucial to always keep an eye on your BP. Keep a BP monitor at home always. There are lot of BP monitors available in offline and online market you can choose a good one out of them. If you ask me, below here could be the good options to go with, based on my experience.




If you looking some cheaper alternatives, you could go with any one of these below





16 Proven Health Benefits of Coffee (Caffeine)
High Blood Uric Acid – Risks, Tests, Treatments
Arthritis, Joint Pain, Arthritis Types, Symptoms, Causes, Risks, Diagnosis, Arthritis Treatment