In this article we have a closer look on arthritis, joint pain, arthritis types, symptoms, causes, risks, arthritis diagnosis, arthritis treatment medicine, treatment therapies and other facts about it.
What is Arthritis?
It is a joint disorder causing joint inflammation and joint pain in our body. A joint is an area of the body where two different bones meet together to get the body parts connected. Joints help body making movements at the joint area and Arthritis is the inflammation of one or more joints. To clarify, there are over 100 types of this disease; Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout and systemic lupus erythematosus are few common types of Arthritis. It can affect one or more joints. While the word “Arthritis” is referred to joint pain and join inflammation, the term is commonly used to describe more than 100 rheumatic diseases and conditions. These diseases and conditions could either affect the joints, tissues that surround the joint or the other connecting tissue.
Though there are more than 100 different arthritis types with different arthritis causes and arthritis treatment methods, the two most common types of arthritis are Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Remember, often the pain in heel is assumed as arthritis pain but this is more likely to be due to plantar-fasciitis.
The symptoms usually develop over time, but may also appear as a sudden onset. Arthritis pain is more common in women than men especially in those who are overweight but may develop in men as well. It is more commonly seen in people over the age of 65 but it can also develop in children, teens and younger adults.
Arthritis Symptoms and Warning Signs
As there is a wide range of types of Arthritis diseases so the symptoms can vary depending on the specific type of disease. The warning signs may include joint pain, swelling, stiffness and difficulty in moving a joint. This is most often a chronic disease and the symptoms may appear frequently or may develop gradually and persist over time.
Though there could be specific symptoms associated with specific types of Arthritis, there are four key warning signs in general. So you should see your doctor if you feel any of these symptoms:
1. Joint Pain – Pain in affected joint or area is the basic symptom. The pain can either be constant or frequent and may come and go.
2. Redness or Swelling – In some types it can cause swelling or redness over skin of affected joint.
3. Stiffness in Joints – Joints stiffness is also a typical symptom.
4. Difficulty in Moving Joint – You can feel difficulty in moving a joint for example while getting up from a chair or while bending.
Insulin Resistance – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Complications and Treatments
Prediabetes – Causes, Symptoms, Complications and Treatments
Diabetes Mellitus, Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Causes, Treatments
Important Arthritis Facts
Here are few important facts to know about this disease.
1. “Arthritis” is a common name used to describe more than 100 rheumatic diseases and conditions which affect the joints.
2. About 1 out of every 5 US adults has doctor-diagnosed arthritis.
3. About half of US adults with heart diseases (49%) or Diabetes (47%) also have arthritis.
4. This is the leading cause of “Disability” in US and can affect a person’s ability to perform daily routine tasks.
5. Being physically active causes a positive effect on arthritis cure and hence can improve the joint pain, function and mental health of the patient.
6. There are many causes and risk factors contributing to the development of this disease. For example it can include diabetes, persistent prediabetes, injury, abnormal metabolism, inheritance from ancestors, infections and immune system dysfunction.
7. At at a later stage there is no permanent treatment except join replacements in some cases though can me managed with a combination of exercise, physical therapies and medications.
8. Arthritis is the joint inflammation of one or more joints typically characterized by joint pain, swelling around one or more joints, stiffness in joints and limited function of joints. However symptoms can develop gradually or suddenly.
9. Though very common join disease in old age women but it can attack men, women, children and adults.
10. Early and accurate diagnosis can help in prevention from being it a chronic disease, irreversible damage and disability which is the major complication of it.
11. Chronic diseases are the disease which persists for longer than 3 months and mostly caused by our inactive life style, bad food habits and being overweight. Some dangerous chronic disease are insulin resistance, prediabetes, diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Weight Loss Diet – 12 Foods to Lose Weight Naturally
Arthritis Causes and Risk Factors
Joints in our body are connected with a firm but flexible connective tissue called Cartilage. The Cartilage protects the joints by absorbing the pressure and shock created when we move and put stress on the joints. A reduction in the normal amount of this cartilage tissue increase risks and may cause some forms of it.
The most common form of Arthritics i.e. Osteoarthritis (OA) is caused by normal wear and tear of cartilage. Though there is no single cause of all types of arthritis and there could be different causes for different types of Arthritis.
We can classify the risk factors into two categories; one which we can control i.e. “Controllable Risk Factors” and other which we cannot control i.e. “Uncontrollable Risk Factors”.
Controllable Arthritis Risk Factors
Being Overweight – Excessive weight and obesity can cause the Arthritis in both men and women and is the leading cause of both the onset and progressive knee osteoarthritis. So it is recommended that you keep your weight under control with regular exercise and eating healthy food to lose weight.
Diet and Nutrition – Although the specific foods and food sensitivities are not known to cause arthritis but diet and nutrition can play an important role in managing risks.
As a simple rule, foods which increase inflammation in our body can worsen the disease; such as animal derived foods and diets high in refined sugar. Gout is a type of arthritis which is caused by the elevated levels of uric acid. The elevated uric acid can be a result of a diet high in purines such as seafood, red wine and other meats.
Joint Injuries – For instance, some injuries to the joints can contribute to development of degenerative arthritis Osteoarthritis.
Abnormal Metabolism – Disturbed metabolism can also cause some certain types of this disease including Gout and Pseudogout.
Infection – Sometimes some infections can also affect the joints and can cause various forms of it.
Smoking – It can also lead to develop some certain types of arthritis.
Occupation and Living Style – Certain living style and occupation behaviors can also cause repetitive knee bending and squatting which can lead to develop the Osteoarthritis.
Uncontrollable Arthritis Risk Factors
Growing Age – It is common in older people having age 65 or more and the risk of developing most type of arthritis increases with the growing age. Osteoarthritis is generally caused by a reduction in cartilage tissue through wear and tear over the life.
Gender – Arthritis pain is more common in women and 60% of all people with arthritis are female.
Inheritance – Arthritis such as Osteoarthritis can also be inherited from ancestors.
Genetic and Immune System Dysfunction – Some people with some certain genetic traits may be more susceptible to certain arthritic conditions such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder and occurs when our body’s own immune system attacks the tissues of body. This affect the Synovium and can eventually lead to the destruction of both the bone and cartilage inside the joint.
To clarify, Synovium is a soft tissue in our joints which produces a fluid to keep the cartilage nourished and the joints lubricated
Arthritis Types
There are number of varieties of Arthritis and join pains; more than 100 types have been identified and the number is still growing.
Types could range from those which are related to wear and tear of cartilage such as Osteoarthritis to those which are associated with joint inflammation resulting from attack of an overactive immune system such as Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Over all the diseases is classified into seven major groups including
- Degenerative or Mechanical Arthritis
- Inflammatory Arthritis
- RA (Rheumatoid)
- Soft Tissue Musculoskeletal Pain Arthritis
- Back Pain Arthritis
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Infectious Arthritis
- Metabolic Arthritis
1. Degenerative or Mechanical Arthritis
Joints in our body are connected with a firm but flexible connective tissue called Cartilage. The Cartilage protects the joints by absorbing pressure and shocks. In Degenerative or Mechanical Arthritis the cartilage is damaged causing the cartilage to become thinner and rougher. This results in joint pain while movements of joints happen.

As a natural phenomenon, our body tries to compensate that loss of cartilage and attempts to restore the stability by remodeling the bone. As a result of this remodeling of bone can cause in undesirable growth of bone to develop Osteophytes. This condition is commonly called Osteoarthritis. To clarify, symptoms of Osteoarthritis are usually a result of wear and tear of cartilage on the joints overtime. It means that the joints which have been overworked are more affected than others.
Osteoarthritis is the major Degenerative Arthritis and there are an estimated 26.9 million adults living with osteoarthritis in the US.
Symptoms may include pain and stiffness in the joints, pain that becomes worse after exercise or pressure on the joint, Rubbing, grating or crackling sound when a joint is moved, morning stiffness and pain that causes sleep disturbances.
2. Inflammatory Arthritis
Though the inflammation is a natural reaction of our body caused as the healing process and as a defense against viruses and bacteria attacks or as a response to injuries. But in case of Inflammatory Arthritis, the inflammation occurs without any apparent reason. Such joint inflammation is not required for body and instead causes damage in the affected joints which results in joint pain, swelling and stiffness in joints. The most occurred Inflammatory arthritis include:
3. RA (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
This is one of the most common type of Arthritis. And there are an estimated 1.5 million adults in the US affected with Rheumatoid Arthritis.

Rheumatoid is caused by persistent inflammation in the synovia which leads to the degeneration of cartilage and bone and eventually leads to joint deformity, pain, swelling and redness. Rheumatoid Arthritis can cause the permanent disability and even premature mortality, in some cases.
Key Symptoms of Rheumatoid include Morning stiffness, Joint pain, chest pain when taking a breath (pleurisy), dry eyes and mouth (Sjögren’s syndrome), blurry vision and Sleep difficulties. Over time, joints may lose their range of motion and may become deformed.
Few other examples of Rheumatoid are Reactive Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis and Arthritis associated with colitis or psoriasis.
4. Soft Tissue Musculoskeletal Pain
When the pain is felt in tissues other than the joints and bones, this is called Soft tissue musculoskeletal pain such as pain in tennis elbow. The soft tissue musculoskeletal pain originates from the soft tissues or muscles which support the joints.
5. Back Pain
There could be a number of reasons causing back pain including “slipped disc” (as it could be in case of osteoporosis which leads to thinning of the bones), nerves issues, pain in bones and joints, pain in ligaments etc.
Back pain may also occur as a result of osteoarthritis when it occurs in the spine, often called spondylosis. In many cases your doctor may be unable to identify the exact cause of back pain and such condition is called as “non-specific” pain.
6. Connective Tissue Disease (CTD)
Connective tissues are the tissues which support, bind together or separate other body tissues and organs such as tendons, cartilages and ligaments. Though CTDs (Connective Tissue Diseases) are associated with joint pain but the CTD inflammation may also occur in other body tissues including the lungs and kidneys, skin and muscles. Connective Tissue Diseases can include Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) and Dermatomyositis.

7. Infectious Arthritis
This disease can sometimes caused by a bacterium, virus or fungus infection. This infection can affect the joints and cause inflammation in joint area. Examples of Infectious arthritis include Salmonella and Shigella (food poisoning or contamination), Chlamydia and gonorrhea (sexually transmitted diseases) and Hepatitis C (a blood-to-blood infection).
8. Metabolic Arthritis
Gout is the most common metabolic arthritis. Increased Uric acid level in some people forms needle-like crystals in the joint. This crystallization results in sudden spikes of extreme joint pain or called a Gout Attack. Gout initially can come occasionally but if the elevated level of Uric acid is not treated, it can become a Chronic Disease.
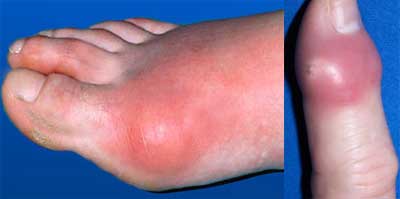
There are around 8.3 million individuals who suffer from Gout each year in the US. There are many risk factors associated which could contribute to the development of Gout arthritis including consumption of alcohol, being overweight, use of Diuretics, over consumption of seafood and meet, hypertension and poor kidney function.
Key symptoms of Gout arthritis include sudden pain in knee, ankle joints especially during the night, feeling warm, tender and redness near joint and occasional fever.
Arthritis Diagnosis
Your doctor will start with the physical exam for diagnosis of Arthritis. Diagnosis depends on the type of arthritis suspected. Here are some of the tests associated with different types of conditions.
1. Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis
In most cases there is no lab test required to diagnose Osteoarthritis and your doctor will start with a physical exam if suspect for osteoarthritis; the physical exam can be conducted to identify if:
- A joint has the limited range of motion
- The patient feel pain upon normal joint movements.
- Feel tenderness when the joint is pressed
- Joint movement causes a crackling sound (crepitation)
- There is a swelling around the joint
- The bones around the joints feel little larger than normal
Imaging Scan Tests – The imaging tests for diagnosis may include X-ray, Ultrasound or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan to look for joint damage.
Joint Fluid Analysis – Your doctor may examine if there’s inflammation present or if the pain is caused by gout or an infection by diagnosing the joint fluid. The joint fluid can be extracted from affected joint using a needle.
Blood Tests – Though the blood test is not required for Osteoarthritis diagnosis but sometimes your doctor may suggest it to check the other causes of joint pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
If your doctor in a primary examination suspect of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), you could be referred to rheumatologist. Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis is a difficult task and there is no single test that can confirm Rheumatoid. To make a proper diagnosis, the rheumatologist may ask questions about individual and family medical history, perform physical exam and then order the arthritis diagnostic tests.
Blood Tests – The diagnosis for Rheumatoid may require to conduct blood tests to measure inflammation level (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR, or “sed rate”) and C-reactive protein (CRP)) and antibodies.
Imaging Tests – Apart from blood tests some imaging tests may also be performed including X-ray, Ultrasound or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan to look for joint damage.
3. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis (SLE)
There is no single test for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) diagnosis because it affects different people in different ways. Lupus is generally identified through a combination of clinical and laboratory criteria.
Your doctor will diagnose Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with a sequence of tests which includes physical exam, asking questions, conducting some blood and urine tests.
Blood Tests – Lab diagnosis for Lupus will include Blood tests (Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, Anti-nuclear antibody test, Anti-DNA antibody test, Complement level test etc.)
Imaging Tests – Imaging tests to diagnose Systemic Lupus Erythematosus may include X-ray, Ultrasound or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan.
Arthritis Treatments
There are two objectives of arthritis treatment; one is to manage and control the pain and second to make sure that no further damage or arthritis complication will happen.
Whether you have inflammatory or non-inflammatory arthritis, there could be a variety of treatments applicable including
Medication
There are varieties of medication available for arthritis treatment; a few of them are:
1. Analgesics medications – Such as Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or Hydrocodone (Vicodin). These medicines are however effective for pain management but do not decrease the inflammation.
2. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – Some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help in controlling arthritis pain and inflammation
3. Corticosteroids or DMARDs– Your doctor may suggest some Corticosteroids or Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) to suppress your immune system in case of Rheumatoid.
4. Ointments – Few ointments such as capsaicin or menthol creams can block the transmission of pain signals from your joints and provides relief from pain.
Joint Surgery
In case of severe arthritic conditions especially related to hips and knees, doctors can recommend Surgery to replace your joint with an artificial one.
Physical Therapy
One way to overcome the arthritis pain is to strengthen muscles around the affected joints. Doctors suggest to adopt some physical therapies involving strengthening exercises. Your doctors may suggest below physical therapies:
Physical Exercise Therapy – It includes some specific exercises customized to the condition of disease often in combinations of other arthritis treatments such as massage or ice & hot packs.
Warm Water Therapy – In this arthritis treatment therapy exercise is done in a pool of warm-water. The warm water reduces the pressure from joints.
Occupational therapy – It involves suggestions and practical advice on how to manage your daily tasks and what precautions are to be followed during your routine work. It also suggests selecting specialized aids and equipment and keeping your joints protected from further damages.
Being Physically Active
Though people with arthritis can feel a short term increase in joint pain while increasing the level of exercise but if you continue exercise the pain will be reduced by the time.
There are many joint friendly exercises that your physiotherapist can suggest and sometimes customize for your specific disease condition. Some of the joint friendly physical activities for adults with arthritis may include Swimming, walking or riding a bike.
Self-management
If you are an Arthritic, being only on medication is not enough. Self management of arthritis is also important and plays a vital role in making your life quality better. Stay physically fit and active, keep your weight under control and protect your joints from unnecessary stress, take proper sleep and eat a healthy and nutritious diet. Do not sit for long and keep taking regular shorter breaks while sitting for long.
Chronic Diseases – The Leading Causes of Death and Disability
Diabetes Cure Is A Reality Now – Reverse Type 2 Diabetes
Plantar Fasciitis – Symptoms, Cause, Complications and Treatments